EMS Landing page
Alerts and notifications are important features of Microsoft Intune. You can see at a glance if there are issues in your environment (alerts) and you can be informed of alerts without even looking at the console (notifications).
Alerts
See the Alerts Overview (Alerts > Overview) which contains a summary of alert types. There are a number of alerts in my Intune test lab at the moment.
You can view by date, category or severity.
Click All Alerts to see the current alerts. Highlight an alert to see the details. I see that I have a problem with one of my policies being applied to devices. The description tells me what I need to know. There seems to be an error connecting to my Exchange server and this has an obvious effect on my conditional access policies. I know that currently there is a problem with my Intune Connector so I better fix that when I get a chance.
This particular alert (policy deployment delayed) could possibly be caused by an Intune issue. Click "View troubleshooting information".
This brings us to the Microsoft Intune Service Dashboard and we can quickly see if there are any service issues at this time. All looks good for now.
What is an alert type?
An Alert Type is a predefined rule that monitors and responds to "a specific system or software state". Microsoft Intune comes with a set of default alert types that you can customize. An alert displays when the requirements of the alert type are met. Multiple alerts can be generated from a single alert type.
Click "Configure Alert Type Settings" on the Overview page.
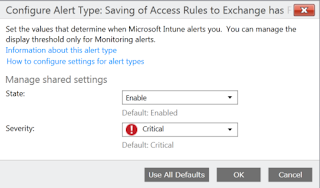
This brings us to Administration > Alerts and Notifications > Alert Types. There are 185 preconfigured Alert Types. See the different Categories and Severity settings. Some are enabled by default. (Note that you cannot configure your own Alert Type).
There are a number of Mobile Device Management and Policy Alert Types for example.
Right click any of the types to enable/disable or to configure.
You can change the severity of the type.
Some Alert Types allow you to configure a Display Threshold (percentage).
Others have additional specific settings.
You can close an alert at any time from the right click menu.
Click Alerts > All Alerts > Notices
Important Intune Service announcements are displayed here.
Notifications
First let's add a recipient for the notification. Navigate to Administration > Alerts and Notifications > Recipients. Click to Add the recipient
Enter the recipient email address.
The recipient has been created.
Navigate to Administration > Alerts and Notifications > Notification Rules
These are the default rules. Highlight a rule and choose "Select Recipient"
Choose the required recipient. Pat will now be notified by email for all alerts. To prevent alert notification emails from being classified as junk email, it may be required to add Microsoft Intune (Windows.Intune@Microsoft.com) to the list of safe or trusted senders in your email environment.
See that you can create your own custom notification rule. Click "Create New Rule".
Choose your required categories and severity level.
Choose the device groups you want.
Choose your recipient and save the rule.
I hope that this information is useful. This is a very important Intune feature for me.
Saturday 13 June 2015
Monday 8 June 2015
Cloud storage with Microsoft Intune
EMS Landing page
I'd like to share some information on cloud storage with Microsoft Intune. When you sign up for a free trial you are assigned 2GB of storage. You get 20GB with a paid subscription. If this is not enough you can purchase additional storage at 1GB increments by using the Microsoft Intune Extra Storage Add-on. The following rules apply:
But what is this storage used for? Intune Cloud storage is consumed by the following:
Intune cloud storage is NOT consumed for the following:
See the cloud storage consumed in my lab environment.
I'd like to share some information on cloud storage with Microsoft Intune. When you sign up for a free trial you are assigned 2GB of storage. You get 20GB with a paid subscription. If this is not enough you can purchase additional storage at 1GB increments by using the Microsoft Intune Extra Storage Add-on. The following rules apply:
- You cannot purchase additional storage during any Intune pre-release or trial period.
- You must have an active paid subscription in order to purchase additional storage.
- Only billing administrators or global administrators for your Microsoft Online Service can purchase additional storage through the Intune account portal. To add, delete, or manage these administrators, you must be a global administrator and sign in to the Intune account portal.
- If you are a volume licensing customer who has purchased Intune or the Microsoft Intune Add-on through the enterprise agreement, contact your Microsoft Account Manager or Microsoft Partner for pricing information and to purchase additional storage.
But what is this storage used for? Intune Cloud storage is consumed by the following:
- Deployed Line of Business Applications
- Deployed custom applications
- Deployed software updates
Intune cloud storage is NOT consumed for the following:
- Applications with deep links to an online store
- Intune policies
- Device inventory
See the cloud storage consumed in my lab environment.
Thursday 4 June 2015
Azure RMS and SharePoint Online
EMS Landing page
Have a look a this document which describes in detail how to configure Information Rights Management for SharePoint Online.
Set up Information Rights Management (IRM) in SharePoint admin center
Choose Admin > SharePoint. You’re now in the SharePoint admin center.
Then choose Refresh IRM Settings.
To apply additional restrictions to the documents in this list or library, click Show Options.
That's it. You have now configured Information Rights Management to protect SharePoint Online documents - simple.
Have a look a this document which describes in detail how to configure Information Rights Management for SharePoint Online.
Set up Information Rights Management (IRM) in SharePoint admin center
Sign in to the
Office 365 Admin Center
Choose Admin > SharePoint. You’re now in the SharePoint admin center.
Choose Settings. On
the Settings page, in the Information Rights Management (IRM) section, choose
"Use the IRM service specified in your configuration".
Then choose Refresh IRM Settings.
Go to the list or
library for which you want to configure IRM.
On the ribbon, click
the Library tab, and then click Library Settings (If you are working in a list,
click the List tab, and then click List Settings).
Under Permissions
and Management, click Information Rights Management.
On the Information
Rights Management Settings page, select the "Restrict permission to documents in
this library on download" check box.
To apply additional restrictions to the documents in this list or library, click Show Options.
That's it. You have now configured Information Rights Management to protect SharePoint Online documents - simple.
RMS Protection Tool
EMS Landing page
Have a look at the RMS Protection Tool which was announced as generally available this week. See the announcement here
"The RMS Protection Tool contains PowerShell Cmdlets designed for developers and IT professionals who want to use scripting mechanisms to bulk protect and unprotect documents".
With this release, you can do the following:
Download the tool from:
https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=47256
The download includes x86 and x64 installers and a PDF file explaining the PoSH cmdlets.
Prerequisites
.Net 3.5
AD RMS Client 2.1
Now run the appropriate installer for the tool and the cmdlets are installed under the module "RMSProtection". Get-Help gets you further information on each cmdlet.
The available cmdlets are as follows:
Get-RMSFileStatus (returns RMS protection status of the specified file or files)
Get-RMSServer (returns the list of all AD RMS servers that can issue templates for the user)
Get-RMSTemplate (returns a list of AD RMS templates)
New-RMSProtectionLIcense (creates and returns a new ad-hoc license from scratch. The license object returned can be used by Protect-RMSFile to encrypt a file or files)
Protect-RMSFile (protects using RMS encryption the specified file or the files in a specified folder)
Unprotect-RMSFile (unprotects using RMS encryption the specified file or the files in a specified folder)
Get-RMSServerAuthentication (gets the status of the S2S credentials - shows the credentials previously set by Set-RMSServerAuthentication)
Set-RMSServerAuthentication (sets the status of the S2S credentials)
Have a look at the RMS Protection Tool which was announced as generally available this week. See the announcement here
"The RMS Protection Tool contains PowerShell Cmdlets designed for developers and IT professionals who want to use scripting mechanisms to bulk protect and unprotect documents".
With this release, you can do the following:
- Use admin-defined templates and ad-hoc policies to protect documents.
- Protect documents of any type - Office file formats, PDFs, text, images, and generic file protection.
- Use the Cmdlets on Azure RMS and on-premises AD RMS.
- Service-to-service authentication for Azure RMS scenarios - for server workloads, it is important that the application is authenticated silently, which can be achieved using these Cmdlets.
Download the tool from:
https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=47256
The download includes x86 and x64 installers and a PDF file explaining the PoSH cmdlets.
Prerequisites
.Net 3.5
AD RMS Client 2.1
Now run the appropriate installer for the tool and the cmdlets are installed under the module "RMSProtection". Get-Help gets you further information on each cmdlet.
The available cmdlets are as follows:
Get-RMSFileStatus (returns RMS protection status of the specified file or files)
Get-RMSServer (returns the list of all AD RMS servers that can issue templates for the user)
Get-RMSTemplate (returns a list of AD RMS templates)
New-RMSProtectionLIcense (creates and returns a new ad-hoc license from scratch. The license object returned can be used by Protect-RMSFile to encrypt a file or files)
Protect-RMSFile (protects using RMS encryption the specified file or the files in a specified folder)
Unprotect-RMSFile (unprotects using RMS encryption the specified file or the files in a specified folder)
Get-RMSServerAuthentication (gets the status of the S2S credentials - shows the credentials previously set by Set-RMSServerAuthentication)
Set-RMSServerAuthentication (sets the status of the S2S credentials)
Wednesday 3 June 2015
Role Based Access to Microsoft Intune
EMS Landing page
An exciting new feature was added to Microsoft Intune this month (Intune version 5.0.5161.0). An additional "helpdesk role" was added to filter the view of the Intune admin console and only provide access for helpdesk staff to perform remote tasks.
Have a look at the Intune Team blog to read about this and the other new features announced.
http://blogs.technet.com/b/microsoftintune/archive/2015/05/19/android-app-wrapping-tool-plus-new-features-for-ios-android-windows-phone.aspx
In this blog I will have a look at the administrative roles that are now available in Microsoft Intune.
Launch the Intune console and navigate to Admin > Administrator Management > Service Administrators. Select to Add a new Administrator. A new role is now available - Helpdesk - Groups Role.
Add a new Helpdesk Administrator (Tom)........
......and also add a Read-Only Administrator (Pat) so that we can verify what each has permissions to do.
Let's first remind ourselves what "Full Access" looks like.
Now log into the Intune console as Tom.
This is the limited console view of the new "Helpdesk Administrator". It is not possible to carry out any configuration or policy change.
The Helpdesk Administrator can only perform Remote Lock and Password Reset on the devices.
Now log into the console as Pat. Remember Pat is now a Read-Only Administrator. He will not be able to modify configuration or policies.
He cannot perform management tasks on the devices.
He can however create reports.
Pat can customise the report.
Final report.
I believe that the new "Helpdesk Administrator" role will be very useful addition to the Intune device management capability.
An exciting new feature was added to Microsoft Intune this month (Intune version 5.0.5161.0). An additional "helpdesk role" was added to filter the view of the Intune admin console and only provide access for helpdesk staff to perform remote tasks.
Have a look at the Intune Team blog to read about this and the other new features announced.
http://blogs.technet.com/b/microsoftintune/archive/2015/05/19/android-app-wrapping-tool-plus-new-features-for-ios-android-windows-phone.aspx
In this blog I will have a look at the administrative roles that are now available in Microsoft Intune.
Add a new Helpdesk Administrator (Tom)........
......and also add a Read-Only Administrator (Pat) so that we can verify what each has permissions to do.
Let's first remind ourselves what "Full Access" looks like.
Now log into the Intune console as Tom.
This is the limited console view of the new "Helpdesk Administrator". It is not possible to carry out any configuration or policy change.
The Helpdesk Administrator can only perform Remote Lock and Password Reset on the devices.
Now log into the console as Pat. Remember Pat is now a Read-Only Administrator. He will not be able to modify configuration or policies.
He cannot perform management tasks on the devices.
He can however create reports.
Pat can customise the report.
Final report.
I believe that the new "Helpdesk Administrator" role will be very useful addition to the Intune device management capability.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)